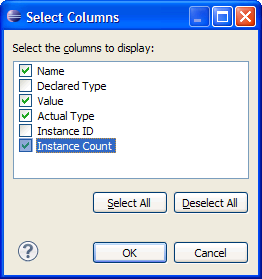
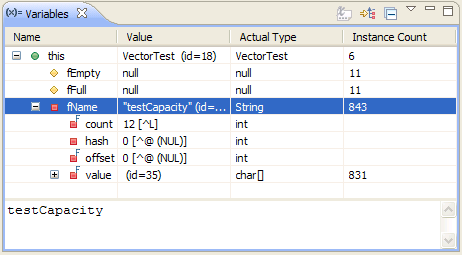
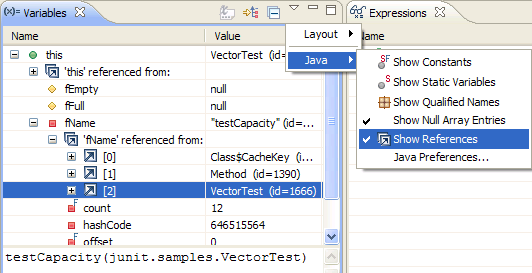
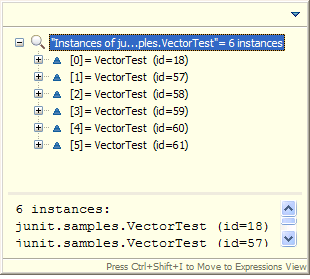
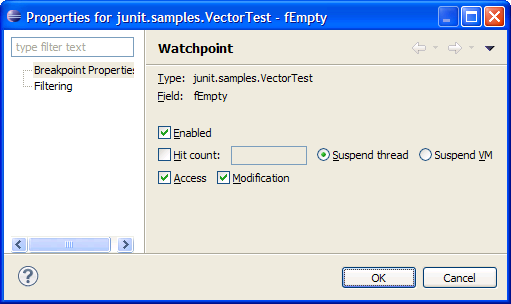
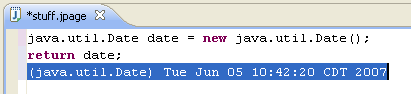
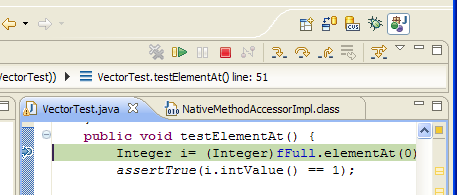
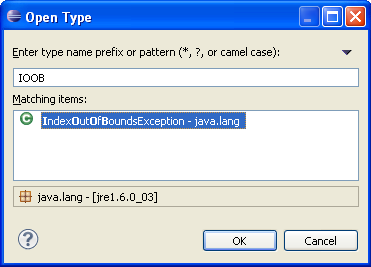
| Content assist |
Content assist provides you
with a list of suggested completions for partially entered strings.
In the Java editor press Ctrl+Space or use Edit >
Content Assist.

|
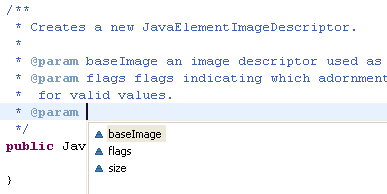
| Content assist in
Javadoc comments |
Content assist is also
available in Javadoc comments.
|
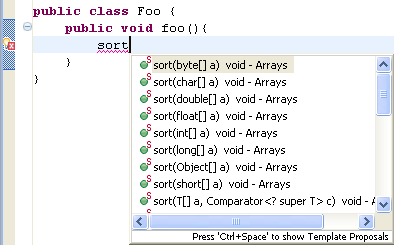
| Content assist for static imports |
To get content assist proposals for static members
configure your list of favorite static members on the
 Java > Editor > Content Assist > Favorites preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist > Favorites preference page.
For example, if you have added java.util.Arrays.* to
this list, then all static methods of this type matching the completion
prefix will be added to the proposals list:
|
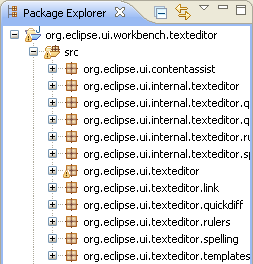
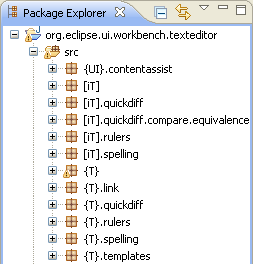
| Suppress types in content
assist |
To exclude certain types from appearing in content assist, use the type
filter feature configured on the
 Java > Appearance > Type Filters
preference page. Types matching one of these filter patterns
will not appear in the Open Type dialog and will not be available to
content assist, quick fix and organize imports. These filter patterns
do not affect the Package Explorer and Type Hierarchy views.
Java > Appearance > Type Filters
preference page. Types matching one of these filter patterns
will not appear in the Open Type dialog and will not be available to
content assist, quick fix and organize imports. These filter patterns
do not affect the Package Explorer and Type Hierarchy views.

|
| Content assist for
variable, method parameter and field name completions |
You can use content assist to speed up the creation of fields, method
parameters and local variables. With the cursor positioned after the
type name of the declaration, press Ctrl+Space or use Edit > Content Assist.

If you use a name prefix or suffix for fields, local variables or
method parameters, be sure to specify this in the
 Java > Code Style
preference page.
Java > Code Style
preference page.
|
| Content assist for variable with unresolved type
|
Code assist also works on accesses to
types that are not imported yet. Depending on the
 Java > Editor > Content Assist
> Add import instead of qualified name preference the editor
will either automatically add imports or fully qualify the types for such
proposals.
Java > Editor > Content Assist
> Add import instead of qualified name preference the editor
will either automatically add imports or fully qualify the types for such
proposals.
Pressing ; in the following scenario:
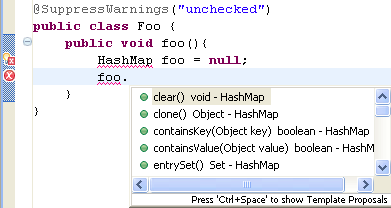
results in:
|
| Content assist after instanceof condition |
Content assist can propose members
available on types used in instanceof conditions.
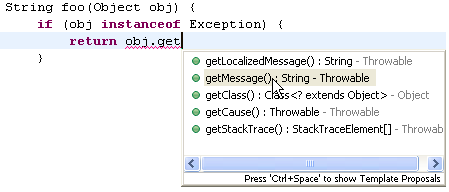
Eclipse will add the required cast for you when you select such a proposal.
|
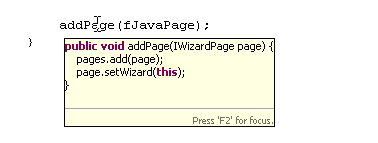
| Parameter hints |
With the cursor in a method
argument, you can see a list of parameter hints. In the Java Editor
press Ctrl+Shift+Space or invoke Edit > Content Assist > Parameter Hints.

|
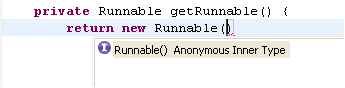
| Content assist on
anonymous classes |
Content assist also
provides help when creating an anonymous class. With the cursor
positioned after "new " and the beginning of an abstract class or interface name
press Ctrl+Space or invoke Edit > Content Assist > Default.

This will create the body of the anonymous inner class including all
methods that need to be implemented.
This also works if you place the caret after the opening parentheses of a class instance creation:
|
| Toggle between
inserting and replacing content assist |
When content assist is invoked
on an existing identifier, it can either replace the
identifier with the chosen completion or do an insert. The
default behavior (overwrite or insert) is defined in the
 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
You can temporarily toggle the behavior while inside the content
assist selection dialog by pressing and holding the Ctrl key while
selecting the completion. |
| Incremental content assist |
Content assist can also Insert common prefixes automatically, similar to
Unix shell expansion. To enable that behavior, select the check box on the
 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
|
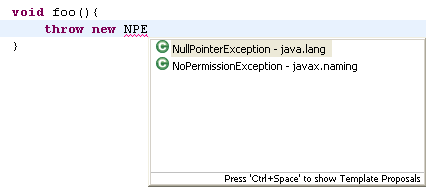
| Camel case support in code completion
|
Code completion supports camel case patterns.
For example, completing on NPE or NuPoiE will propose NullPointerException.
This support can be disabled using the Show camel case matches
preference on the
 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
|
| Use ';' key to insert method invocation
|
You can use the semicolon (;) key to select any method invocation proposal from the content assist popup.
The ';' will be appended at the end of the method invocation.
|
| Customize content assist categories
|
Repeatedly invoking content assist (Ctrl+Space) cycles through different proposal
categories.
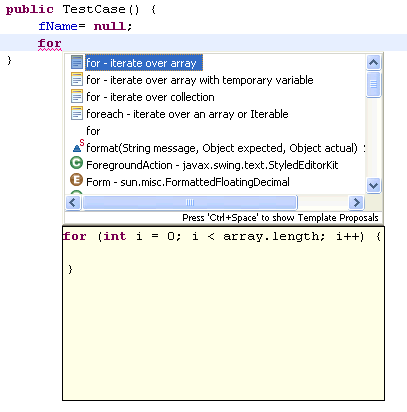
To configure which categories to show use the
 Java > Editor > Content Assist > Advanced preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist > Advanced preference page.
You can also assign separate key shortcuts to your favorite proposal categories.
|
| Create getters and
setters |
To create getter and setter
methods for a field, select the field's declaration and invoke Source
> Generate Getter and Setter.

If you use a name prefix or suffix be sure to specify this in the
 Java > Code Style
preference page.
Java > Code Style
preference page. |
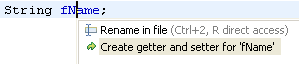
| Create getters and setters quick assist |
A quick assist (Ctrl+1) is available on fields to
create getters and setters.
|
| Use content assist to
create getter and setters |
Another way to create
getters and setters is using content assist. Set the cursor in the
type body between members and press Ctrl+Space to get the proposals
that create a getter or setter method stub.
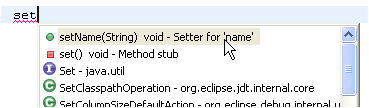 |
| Delete getters and
setters together with a field |
When you delete a field
from within a view,
Eclipse can propose deleting its Getter and Setter methods.
If you use a name prefix or suffix for fields, be sure to specify this in the
 Java > Code Style
preference page.
Java > Code Style
preference page. |
| Create delegate methods |
To create a delegate method
for a field select the field's declaration and invoke Source >
Generate Delegate Methods. This adds the selected methods
to the type that contains a forward call to delegated methods. This
is an example of a delegate method:

|
Create hashCode() and equals()
|
To create the methods hashCode() and equals()
invoke Source > Generate hashCode() and equals().
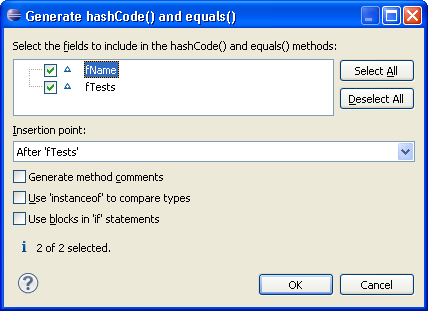
|
| Use templates to create
a method |
Templates are shown together with the Content
Assist (Ctrl+Space) proposals.
There are existing templates, such as 'private_method',
'public_method', 'protected_method' and more, but you can also
define new templates for method stubs.
After applying a template, use the Tab key to navigate among the values to enter
(return type, name and arguments).

|
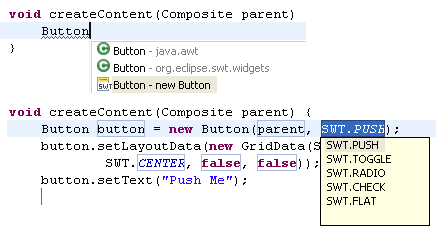
| Use templates to create
SWT widgets |
On projects which have the SWT library on the classpath,
you can create SWT widgets with Content Assist (Ctrl+Space)
To add, for example, an SWT button, type Button and press Ctrl+Space,
select the Button SWT template, and press Enter.
To see all available templates go to the
 Java > Editor > Templates preference page or open the Templates view through Window > Show View > Other....
Java > Editor > Templates preference page or open the Templates view through Window > Show View > Other....
|
| Create your own
templates |
To create your own templates, go to the
 Java > Editor > Templates preference page and press the New button to
create a template. For example, a template to iterate backwards in an
array would look like this:
Java > Editor > Templates preference page and press the New button to
create a template. For example, a template to iterate backwards in an
array would look like this:
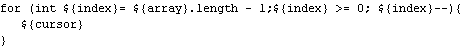
|
| Use Quick Fix to create
a new method |
Start with the method
invocation and use Quick Fix (Ctrl+1) to create the method.

|
| Use Quick Fix to change
a method signature |
Add an argument to a method
invocation at a call site. Then use Quick Fix (Ctrl+1) to add the
required parameter in the method declaration.

|
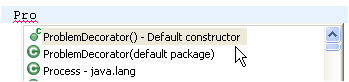
| Use content assist to
create a constructor stub |
At the location where you
want to add the new constructor, use content assist after typing the
first letters of the constructor name.
 |
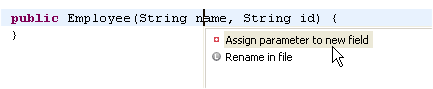
| Create new fields from
parameters |
Do you need to create new
fields to store the arguments passed in the constructor? Use Quick
Assist (Ctrl+1) on a parameter to create the assignment and the
field declaration and let Eclipse propose a name according to your Code
Style preferences.
 |
| Use content assist to
override a method |
Invoke Content Assist
(Ctrl+Space) in the type body at the location where the method
should be added. Content assist will offer all methods that can be
overridden. A method body for the chosen method will be created.
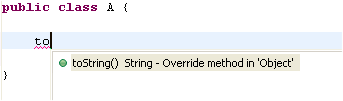
|
| Use Quick Fix to add
unimplemented methods |
To implement a new
interface, add the 'implements' declaration first to the type.
Even without saving or building, the Java editor will underline the
type to signal that methods are missing and will show the Quick Fix
light bulb. Click on the light bulb or press Ctrl+1 (Edit >
Quick Fix) to choose between adding the unimplemented methods or
making your class abstract.
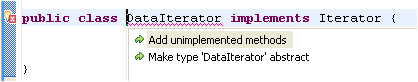
|
| Use Clean Up to add
unimplemented methods |
When you add a new method to
an interface or an abstract method to an abstract class, Eclipse can generate
method stubs in all concrete subclasses at once. Invoke Source > Clean Up...
on a set of Java elements, use a custom profile, and select on the Configure...
dialog to Add unimplemented methods on the Missing Code tab.
|
| Override a method
from a base class |
To create a method that
overrides a method from a base class:
Select the type where the methods should be added and invoke Source >
Override/Implement Methods. This opens a dialog that lets you
choose which methods to override.
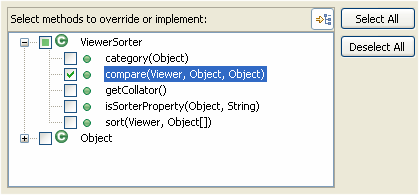
|
| Rename in file | To quickly do a rename that
doesn't require full analysis of dependencies in other files, use the
'Rename in file' Quick Assist. In the Java Editor, position the
cursor in an identifier of a variable, method or type and press Ctrl+1
(Edit > Quick Fix)
The editor is switched to the linked edit mode (like templates) and
changing the identifier simultaneously changes all other references
to that variable, method or type.

You can also use the direct shortcut Ctrl+2 R. Use the
 General > Keys preference page
to configure shortcuts (in the 'Source' category).
General > Keys preference page
to configure shortcuts (in the 'Source' category).
|
| Use Quick Fix to handle
exceptions |
Dealing with thrown exceptions is
easy. Unhandled exceptions are detected while typing and marked with
a red line in the editor.
- Click on the light bulb or press Ctrl+1 to surround the
call with a try catch block. If you want to include more statements
in the try block, select the statements and use Source >
Surround With > Try/catch Block. You can also select individual
statements by using Edit > Expand Selection To and
selecting Enclosing, Next or Previous.
- If the call is already surrounded with a try block, Quick Fix
will suggest adding the catch block to the existing block.
- If you don't want to handle the exception, let Quick Fix add a
new thrown exception to the enclosing method declaration

At any time, you can convert a catch block to a thrown exception. Use
Ctrl+1 (Edit > Quick Fix) on a catch block.
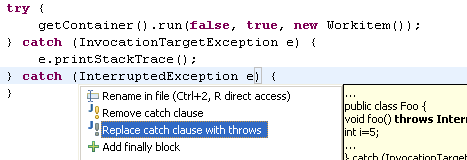
|
| Less typing for
assignments |
Instead of typing an assignment, start
with the expression that will be assigned.
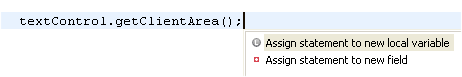
Now use Ctrl+1 (Edit > Quick Fix) and choose 'Assign
statement to new local variable' and Quick Assist will guess a
variable name for you.
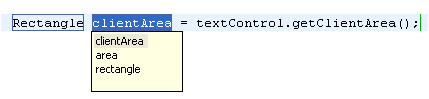 |
| Less work with cast
expressions |
Don't spend too much time with typing casts. Ignore them first and use quick assist to add them after
finishing the statement.
For example on assignments:
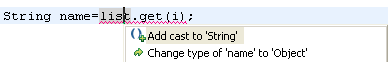
Or for method arguments:

Or for method call targets:
 |
Assign a cast expression
|
After an 'instanceof' check, it is very common to cast the expression and assign it to a new local variable. Invoke Quick
Assist (Ctrl+1) on the 'instanceof' keyword or at the beginning of the block body to save yourself some typing:
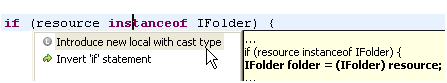
|
| Surround lines |
To surround statements with an if /
while / for statement or a block, select the lines to surround and
invoke Source > Surround With or press Alt+Shift+Z.
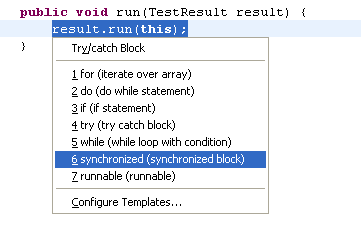
The entries in the menu are derived from the normal editor templates: All
templates that contain the variable ${line_selection} will show up in the menu.
Templates can be configured on the
 Java > Editor > Templates preference page. Edit the corresponding templates to customize the resulting code or
define your own surround-with templates.
Java > Editor > Templates preference page. Edit the corresponding templates to customize the resulting code or
define your own surround-with templates.
|
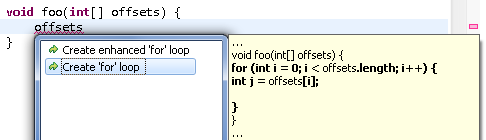
 Create 'for' loops Create 'for' loops |
A set of Quick Assists (Ctrl+1) can create for loops that iterate over a given expression.
For arrays:
- Create an enhanced
for loop
- Create a
for loop using an index
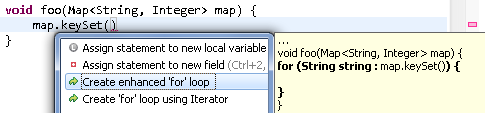
For Collections:
- Create an enhanced
for loop
- Create a
for loop using an Iterator
For Lists:
- Create a
for loop using an index and get(i)
|
 Migrate anonymous class creations to lambda expressions and back Migrate anonymous class creations to lambda expressions and back |
You can convert anonymous class creations to lambda expressions (and back) by invoking the Quick Assists (Ctrl+1):
- Convert to lambda expression
- Convert to anonymous class creation
Before:
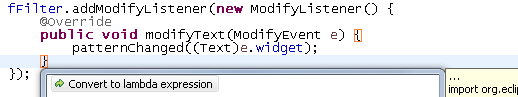
After the Quick Assist (Ctrl+1), the 6 lines are condensed into 1:

Or invoke Source > Clean Up..., use a custom profile, and on the Configure... dialog select Convert functional interface instances
and Use lambda where possible on the Code Style tab.
|
More Quick Assists and Fixes
|
Check out the Quick Assist page for a complete list of available code transformations. A list of quick fixes can be found here.
|
Shortcuts for Quick Fixes and Assists
|
Some of the popular quick assists like
Rename in file and Assign to local variable can be invoked
directly with Ctrl+2 R and Ctrl+2 L. Check
the
 General > Keys preference page for more quick fixes and quick assists that support direct
invocation.
General > Keys preference page for more quick fixes and quick assists that support direct
invocation.
Type "Quick Assist" or "Quick Fix" in the filter field:
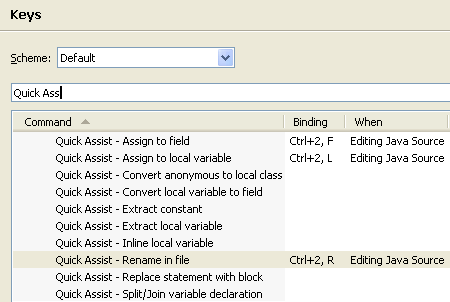
|
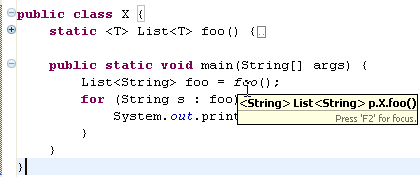
| Content assist can insert
argument names automatically |
You can have content assist insert argument names automatically on
method completion. This behavior can be customized on the
 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page (see the
Fill method arguments and show guessed arguments checkbox.) For example, when
you select the second entry here,
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page (see the
Fill method arguments and show guessed arguments checkbox.) For example, when
you select the second entry here,

content assist will automatically insert argument names:

You can then use the Tab key to navigate between the
inserted names.
If you choose Insert best guessed arguments, the best guess will be filled in by default. The alternative
proposals are still available.
|
Automatically insert
type arguments
|
Enabling Fill method arguments and show guessed arguments on the
 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page
is also useful when working with parameterized types in J2SE 5.0.
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page
is also useful when working with parameterized types in J2SE 5.0.

results in:
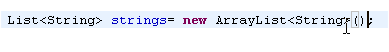
|
Remove type arguments after content assist
|
If content assist added type arguments for a generic type, but you do not want them
because you need the .class literal or you want to invoke a static method,
rather than deleting all the arguments manually,
you can just delete the '<' and that will remove the entire text up to '>'.
|
| Remove surrounding
statement |
To remove a surrounding statement or
block, position the cursor at the opening or closing bracket and press Ctrl+1
(Edit > Quick Fix).

|
| How was that word spelled again? |
You can enable spell-checking support in the Java editor on the
 General > Editors > Text Editors > Spelling
preference page. Spelling errors
are displayed in the Java editor and corresponding Quick Fixes are available:
General > Editors > Text Editors > Spelling
preference page. Spelling errors
are displayed in the Java editor and corresponding Quick Fixes are available:
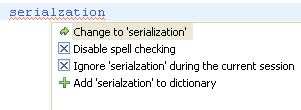
You can make the
dictionary also available to the content assist. A Quick Fix allows you to
add new words to the user dictionary on the fly.
|
| Structured selections |
The Structured Selection actions can be used to
enlarge the current selection to the next enclosing element:
Highlight some text and press Alt+Shift+Arrow Up or select Edit
> Expand Selection To > Enclosing Element from the menu
bar - the selection will be expanded to the smallest Java-syntax
element that contains the selection. You can then further expand the
selection by invoking the action again (or other actions from the Expand Selection To menu).
This is for example helpful to select the enclosing identifier for renames,
or to select adjacent statements for a subsequent Extract Method refactoring.
|
| Find the matching
bracket |
To find a matching bracket select an
opening or closing bracket and press Ctrl+Shift+P or select Navigate >
Go To > Matching Bracket. You can also double click
next to a bracket - this selects the text between the two brackets.

The Java editor also supports highlighting of enclosing brackets.

This can be configured on the
 Java > Editor preference page.
Java > Editor preference page.
|
| Smart Javadoc |
Type '/**' and press Enter. This
automatically adds a Javadoc comment stub containing the standard
@param, @return and @exception tags.

The templates for the new comment can be configured in the
 Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
|
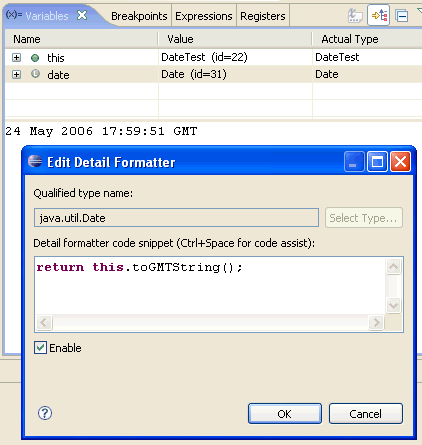
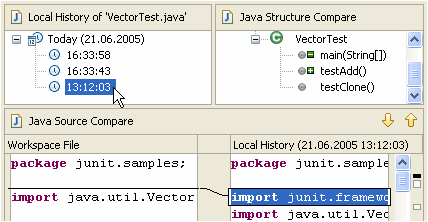
| Use the local history
to revert back to a previous edition of a method |
Whenever you edit a file,
its previous contents are kept in the local history. Java tooling
makes the local history available for Java elements, so you can
revert back to a previous edition of a single method instead of the
full file.
Select an element (e.g. in the Outline view) and use Replace With > Local History
to revert back to a previous edition of the element.
|
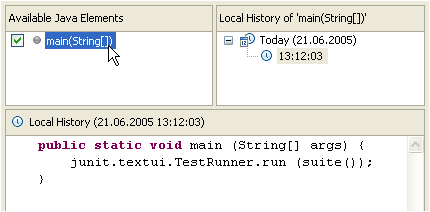
| Use the local history
to restore removed methods |
Whenever you edit a file,
its previous contents are kept in the local history. Java tooling
makes the local history available for Java elements, so you can
restore deleted methods selectively.
Select a container (e.g. in the Outline view) and use Restore from Local History to
restore any removed members.
|
| Customizable code
generation |
The
 Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page
allows you to customize
generated code and comments in a similar way to normal templates.
These code templates are used whenever code is generated.
Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page
allows you to customize
generated code and comments in a similar way to normal templates.
These code templates are used whenever code is generated.
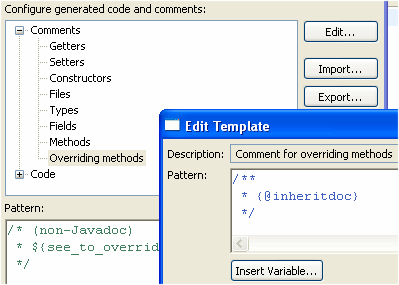
Since 3.1, it is possible to use project specific Code templates, that will also be shared in the team if your project is shared. Open the Properties on a project to enable project specific settings.
|
| Create comments in your
code |
Comments can be added explicitly with Source > Generate Element Comment (Alt+Shift+J) or automatically by various wizards, refactorings or quick fixes.
Configure the comment templates on the
 Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
Enable or disable the automatic generation of comments either directly on the wizard (e.g. using 'Generate
Comment' checkbox on the new Java type wizards) or by the 'Automatically
add new comments for new methods and types' checkbox of the
 Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
All these settings can also be configured on a per project basis. Open the Properties on a project to enable project specific settings. |
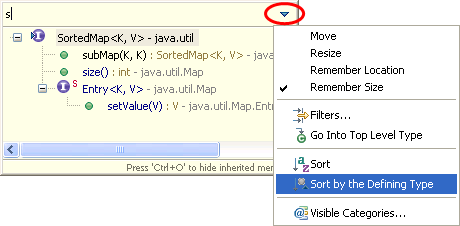
| Sort members |
You can Sort Members
of a Java compilation unit or a set of compilation units according to a category order defined in the
 Java > Appearance > Members Sort Order preference page.
Java > Appearance > Members Sort Order preference page.
You'll find the action under Source > Sort Members. |
| Wrap strings |
You can have String literals wrapped when you edit them. For
example, if you have code like this:
String message= "This is a very long message.";
position your caret after the word "very" and press Enter.
The code will be automatically changed to:
String message= "This is a very" +
" long message.";
This behavior can be customized in the
 Java > Editor > Typing preference page.
Java > Editor > Typing preference page.
|
| Smart Typing and how to control it |
The Java editor's Smart Typing features ease your daily work. You can configure
them on the
 Java > Editor > Typing preference page.
Java > Editor > Typing preference page.
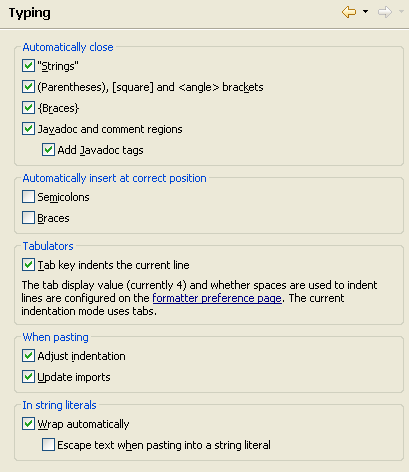
When you enable Automatically insert Semicolons at correct
position, typing a semicolon automatically positions the cursor at the end of the statement before inserting the semicolon. This saves you some additional cursor navigation.
You can
undo this automatic positioning by pressing backspace right afterwards.
|
| Fix your code
indentation with one key stroke |
A useful feature is Source
> Correct Indentation or Ctrl+I.
Select the code where the indents are incorrect and invoke the action.
If nothing is selected, the action indents the current line. |
| Fix your code
indentation on save |
Eclipse can correct the indentation
of your code when you save the editor. Go to the
 Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page and
Configure... Additional actions, and select to Correct indentation on
the Code Organizing tab.
Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page and
Configure... Additional actions, and select to Correct indentation on
the Code Organizing tab.
|
| Quick menus for source and
refactoring actions |
The refactoring and source actions can be accessed via a quick
menu. Select the element to be manipulated in the Java editor or in a
Java view and press Alt+Shift+S for the quick source menu,
Alt+Shift+T for the quick refactoring menu and Alt+Shift+Z for the surround with menu.
|
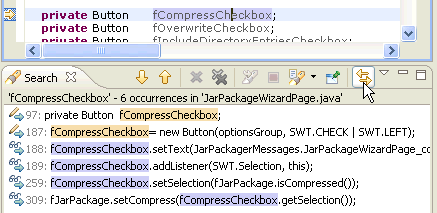
| Find unused code |
The Java compiler detects
unreachable code, unused variables, parameters, imports and unused
private types, methods and fields.
Change the settings for the detection on the
 Java > Compiler > Error/Warnings
preference page. These settings can also be specified per project, use: Project > Properties > Java Compiler >
Error/Warnings.
Java > Compiler > Error/Warnings
preference page. These settings can also be specified per project, use: Project > Properties > Java Compiler >
Error/Warnings.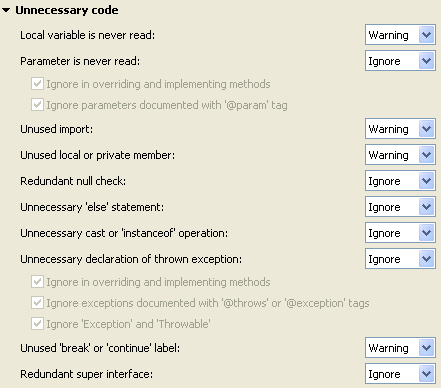
These problems are detected as you type, and a quick fix is
offered to remove the unneeded code.
You can also use Source > Clean Up... to remove unused code. |
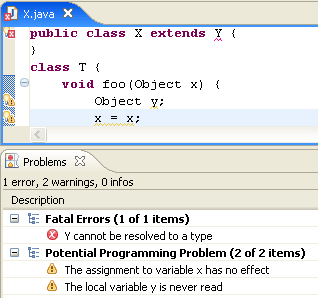
| Find problems with null
|
The compiler can help you find problems with null in your code.
The
 Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings
preference page has three options to detect problems:
Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings
preference page has three options to detect problems:
- Null pointer access (in 'Null analysis')
When this option is enabled, the compiler will issue an error or warning
whenever a variable that is statically known to hold a null value
is used to access a field or method, as shown in the example below:
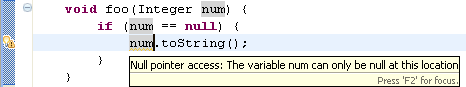
- Potential null pointer access (in 'Null analysis')
When this option is enabled, the compiler will issue an error or a
warning whenever a variable is statically known to potentially hold
a null value, as shown in the example below:
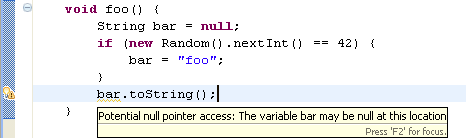
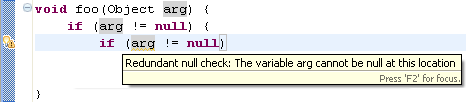
- Redundant null check (in 'Null analysis')
When enabled, the compiler will issue an error or a warning whenever
a variable that is statically known to hold a null or a non-null
value is tested against null, as shown in the examples below:
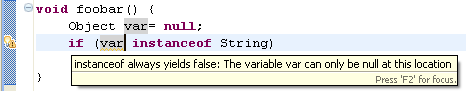
|
| Find problems with externalized strings
|
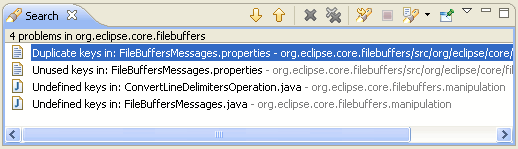
The Source > Find Broken Externalized Strings action
finds undefined, unused and duplicate keys for you:
|
| Change problem severity in problem hover |
When a problem hover has been enriched
(by pressing F2 or moving the mouse into the hover),
an action to change the severity of the current problem is available.
Click on the button in the toolbar to go to the
 Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings preference page.
Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings preference page.
|
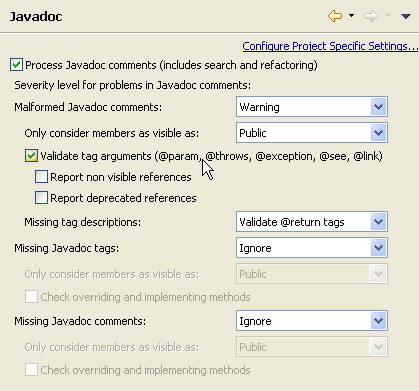
| Javadoc comment handling |
The Eclipse Java compiler can process Javadoc comments. Search
reports references in doc comments, and refactoring updates these
references as well. This feature is controlled from the
 Java > Compiler > Javadoc
preference page (or set for an individual
project using Project > Properties > Java Compiler >
Javadoc).
Java > Compiler > Javadoc
preference page (or set for an individual
project using Project > Properties > Java Compiler >
Javadoc).
When turned on, malformed Javadoc comments are marked in the Java editor and can be fixed using Edit
> Quick Fix (Ctrl+1):
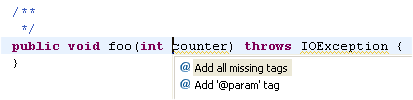
|
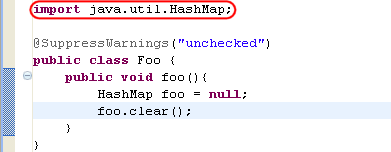
| Suppress warnings |
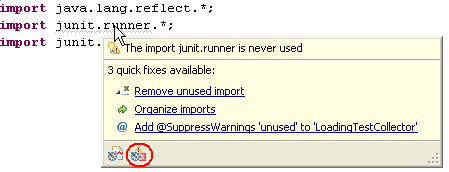
In J2SE 5.0 and later, you can suppress all optional compile warnings using the SuppressWarnings annotation.
In this example, addAll() is marked as an unused method. Quick Fix (Ctrl+1) is used to add a SuppressWarnings annotation so that the warning will not be shown for this method.
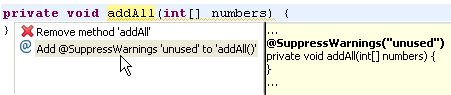
|
| Clean Ups
|
Source > Clean Up... helps fixing multiple
problems at once and helps to establish a consistent code style. For instance, you can:
- convert all
for loops to enhanced for
loops where possible.
- mark all overriding methods in a whole project with an
@Override annotation.
- organize imports
- format your code
- remove unnecessary code
Clean Ups are organized in Clean Up profiles.
A profile can be attached to the workspace or to individual projects.
Project settings can be shared in a team through a version control system.
It is also possible to export and import each profile.
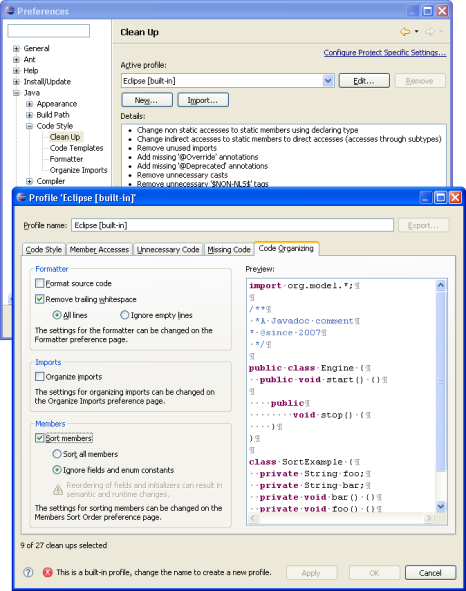
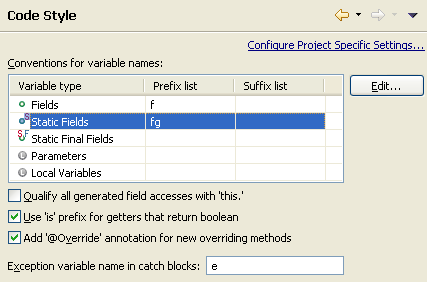
Clean Ups can be executed as save actions on save. Go to the
 Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page to configure
which clean ups to invoke on save.
Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page to configure
which clean ups to invoke on save.
|


 Java > Editor > Content Assist > Favorites preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist > Favorites preference page.

 Java > Appearance > Type Filters
preference page. Types matching one of these filter patterns
will not appear in the Open Type dialog and will not be available to
content assist, quick fix and organize imports. These filter patterns
do not affect the Package Explorer and Type Hierarchy views.
Java > Appearance > Type Filters
preference page. Types matching one of these filter patterns
will not appear in the Open Type dialog and will not be available to
content assist, quick fix and organize imports. These filter patterns
do not affect the Package Explorer and Type Hierarchy views.


 Java > Code Style
preference page.
Java > Code Style
preference page. Java > Editor > Content Assist
> Add import instead of qualified name preference the editor
will either automatically add imports or fully qualify the types for such
proposals.
Java > Editor > Content Assist
> Add import instead of qualified name preference the editor
will either automatically add imports or fully qualify the types for such
proposals.






 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page. Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page.


 Java > Editor > Content Assist > Advanced preference page.
Java > Editor > Content Assist > Advanced preference page.

 Java > Code Style
preference page.
Java > Code Style
preference page.

 Java > Code Style
preference page.
Java > Code Style
preference page.



 Java > Editor > Templates preference page or open the Templates view through Window > Show View > Other....
Java > Editor > Templates preference page or open the Templates view through Window > Show View > Other....
 Java > Editor > Templates preference page and press the New button to
create a template. For example, a template to iterate backwards in an
array would look like this:
Java > Editor > Templates preference page and press the New button to
create a template. For example, a template to iterate backwards in an
array would look like this:
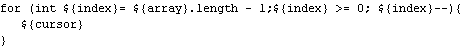








 General > Keys preference page
to configure shortcuts (in the 'Source' category).
General > Keys preference page
to configure shortcuts (in the 'Source' category).









 Java > Editor > Templates preference page. Edit the corresponding templates to customize the resulting code or
define your own surround-with templates.
Java > Editor > Templates preference page. Edit the corresponding templates to customize the resulting code or
define your own surround-with templates. Create 'for' loops
Create 'for' loops Migrate anonymous class creations to lambda expressions and back
Migrate anonymous class creations to lambda expressions and back

 General > Keys preference page for more quick fixes and quick assists that support direct
invocation.
General > Keys preference page for more quick fixes and quick assists that support direct
invocation.

 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page (see the
Fill method arguments and show guessed arguments checkbox.) For example, when
you select the second entry here,
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page (see the
Fill method arguments and show guessed arguments checkbox.) For example, when
you select the second entry here,


 Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page
is also useful when working with parameterized types in J2SE 5.0.
Java > Editor > Content Assist preference page
is also useful when working with parameterized types in J2SE 5.0.
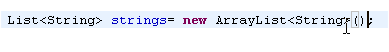

 General > Editors > Text Editors > Spelling
preference page. Spelling errors
are displayed in the Java editor and corresponding Quick Fixes are available:
General > Editors > Text Editors > Spelling
preference page. Spelling errors
are displayed in the Java editor and corresponding Quick Fixes are available:



 Java > Editor preference page.
Java > Editor preference page.

 Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.


 Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page
allows you to customize
generated code and comments in a similar way to normal templates.
These code templates are used whenever code is generated.
Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page
allows you to customize
generated code and comments in a similar way to normal templates.
These code templates are used whenever code is generated.
 Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page. Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page.
Java > Code Style > Code Templates preference page. Java > Appearance > Members Sort Order preference page.
Java > Appearance > Members Sort Order preference page. Java > Editor > Typing preference page.
Java > Editor > Typing preference page. Java > Editor > Typing preference page.
Java > Editor > Typing preference page.

 Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page and
Configure... Additional actions, and select to Correct indentation on
the Code Organizing tab.
Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page and
Configure... Additional actions, and select to Correct indentation on
the Code Organizing tab.

 Java > Compiler > Error/Warnings
preference page. These settings can also be specified per project, use: Project > Properties > Java Compiler >
Error/Warnings.
Java > Compiler > Error/Warnings
preference page. These settings can also be specified per project, use: Project > Properties > Java Compiler >
Error/Warnings.
 Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings
preference page has three options to detect problems:
Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings
preference page has three options to detect problems:






 Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings preference page.
Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings preference page.
 Java > Compiler > Javadoc
preference page (or set for an individual
project using Project > Properties > Java Compiler >
Javadoc).
Java > Compiler > Javadoc
preference page (or set for an individual
project using Project > Properties > Java Compiler >
Javadoc).




 Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page to configure
which clean ups to invoke on save.
Java > Editor > Save Actions preference page to configure
which clean ups to invoke on save.




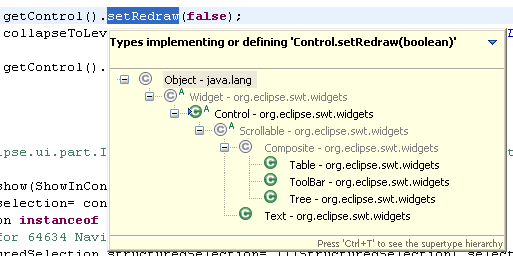
 ).
).


 ) or
press Alt+Shift+O. You'll see within a file, where a
variable, method or type is referenced.
) or
press Alt+Shift+O. You'll see within a file, where a
variable, method or type is referenced.






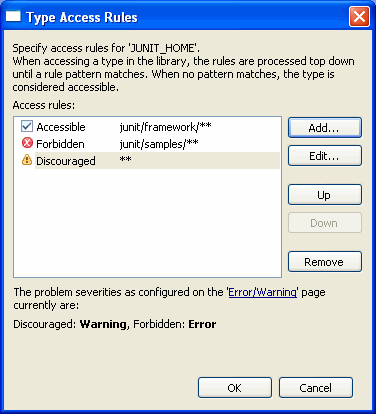
 (the
number of small green squares will grow, indicating progress)
while running them and this icon
(the
number of small green squares will grow, indicating progress)
while running them and this icon  after they are finished. If, however,
errors or failures occur, the icon will change to
after they are finished. If, however,
errors or failures occur, the icon will change to 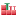 (or
(or  if
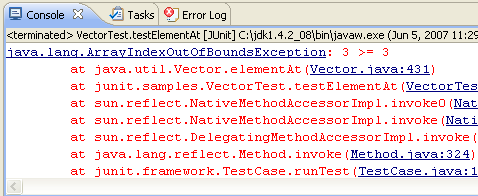
tests are finished) and the JUnit view will appear.
if
tests are finished) and the JUnit view will appear.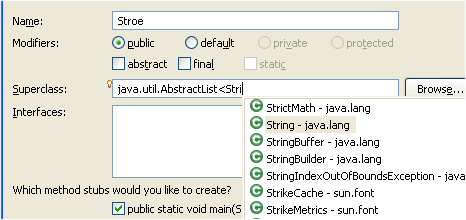








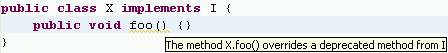



 on Java projects and working sets if they contain build path errors:
on Java projects and working sets if they contain build path errors: